Diagnosis
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) may be diagnosed when a health checkup is done for another reason.
To diagnose AFib, the healthcare professional examines you and listens to your heart. You are usually asked questions about your medical history and symptoms. Tests may be done to look for conditions that can cause changes in the heartbeat, such as heart disease or thyroid disease.
Tests
Tests to diagnose atrial fibrillation (AFib) may include:
- Blood tests. Blood tests are done to look for health conditions or substances that may affect the heart or heartbeat.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test shows how the heart is beating. Sticky patches with sensors on them attach to the chest and sometimes the arms and legs. Wires connect the sensors to a computer, which prints or displays the test results. An ECG is the main test for diagnosing atrial fibrillation.
- Holter monitor. This is a small, portable ECG device. It records the heart's activity. You wear the device for a day or two while you do your regular activities.
- Event recorder. This device is like a Holter monitor, but it records only at certain times for a few minutes at a time. It's worn for up to 30 days or until an irregular heartbeat or symptoms occur. You typically press a button when you have symptoms. Some devices automatically record when an irregular heart rhythm is detected.
- Implantable loop recorder. This device records the heartbeat continuously for up to three years. It also is called a cardiac event recorder. The device shows how the heart is beating while you do your daily activities. It may be used to see how often you have an AFib episode. Sometimes it's used to find rare episodes of AFib in those at high risk of the heart rhythm disorder. For example, you may need one if you've had an unexplained stroke.
- Echocardiogram. Sound waves are used to create images of the beating heart. This test can show how blood flows through the heart and heart valves.
- Exercise stress tests. These tests often involve walking on a treadmill or pedaling a stationary bike while the heart is checked. The tests show how the heart reacts to exercise. If you can't exercise, you may be given medicine that affects the heart like exercise does. Sometimes echocardiogram is done during a stress test.
- Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray shows the condition of the lungs and heart.
More Information
Treatment
The goals of atrial fibrillation (AFib) treatment are to:
- Reset and control the heartbeat.
- Prevent blood clots.
Treatment depends on:
- How long you've had AFib.
- Your symptoms.
- The cause of the irregular heartbeat.
Treatment may include:
- Medicine.
- Therapy to reset the heart rhythm, called cardioversion.
- Heart procedures or surgery.
Together, you and your healthcare team talk about the best treatment option for you. It's important to follow your atrial fibrillation treatment plan. If AFib isn't well controlled, it may lead to complications, including stroke and heart failure.
Medications
Treatment for atrial fibrillation (AFib) may include medicines to do the following:
- Control the speed of the heartbeat.
- Reset the heart rhythm.
- Prevent blood clots, a dangerous complication of AFib.
Medicines may include:
- Beta blockers. These medicines help slow the heart rate.
- Calcium channel blockers. These medicines control the heart rate. But they may need to be avoided by those who have heart failure or low blood pressure.
- Digoxin (Lanoxin). This medicine may control the heart rate at rest, but not as well during activity. Most people need additional or other medicines, such as calcium channel blockers or beta blockers.
- Medicines to control the heart rate and rhythm. Also called anti-arrhythmics, this type of medicine is used sparingly. They tend to have more side effects than other medicines to control the heart rate.
- Blood thinners. Also called anticoagulants, these medicines help prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of stroke. Blood thinners include warfarin (Jantoven), apixaban (Eliquis), dabigatran (Pradaxa), edoxaban (Savaysa) and rivaroxaban (Xarelto). If you take warfarin, you need regular blood tests to check the medicine's effects.
Cardioversion therapy
If atrial fibrillation symptoms are bothersome or if this is the first AFib episode, a treatment called cardioversion may be done to reset the heart rhythm.
Cardioversion can be done in two ways:
- Electrical cardioversion. This method sends electric shocks to the heart through paddles or patches placed on the chest.
- Drug cardioversion. Medicines given through a vein or by mouth are used to reset the heart rhythm.
Cardioversion is usually done in a hospital as a scheduled treatment. But it may be done in emergency situations. If it's scheduled, you may be told to take a blood thinner such as warfarin (Jantoven) for a few weeks before the treatment. The medicine reduces the risk of blood clots and strokes.
After electrical cardioversion, medicines to control the heart rhythm may be needed for life to prevent AFib from returning. Even with medicine, AFib could come back.
Surgery or catheter procedures
AV node ablation
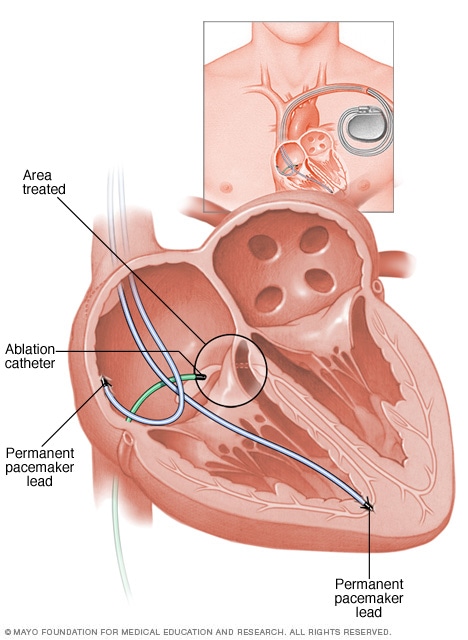
AV node ablation
Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation uses heat energy, called radiofrequency energy, to destroy the area between the upper and lower heart chambers. This area is called the AV node. The heart's electrical signals can't pass through the damaged area. So this treatment blocks the faulty heart signals that cause atrial fibrillation (AFib). Once the AV node is destroyed, a pacemaker is needed to control the heart rhythm.
If AFib doesn't get better with medicine or other treatments, a procedure called cardiac ablation may be necessary. Sometimes ablation is the first treatment.
Cardiac ablation often uses heat or cold energy to create tiny scars in the heart. Heart signals can't pass through the scars. So the treatment can block faulty heart signals that cause AFib. During cardiac ablation, a doctor places a flexible tube called a catheter through a blood vessel, usually in the groin. The doctor guides the tube to the heart. More than one catheter may be used. Sensors on the tip of the catheter apply the cold or heat energy.
Less commonly, ablation is done using a scalpel during open-heart surgery.
There are several types of cardiac ablation. The type used to treat atrial fibrillation depends on your specific symptoms, overall health and whether you're having another heart surgery.
- Atrioventricular (AV) node ablation. Heat energy is usually applied to the heart tissue at the AV node. This destroys the electrical signaling connection. After this treatment, a pacemaker is needed for life.
-
Maze procedure. A doctor uses heat or cold energy or a scalpel to create a pattern of scar tissue in the upper chambers of the heart. The pattern is called a maze. The heart's electrical signals can't pass through scar tissue. So the maze blocks the stray heart signals that cause atrial fibrillation.
If a scalpel is used to create the maze pattern, open-heart surgery is needed. This is called the surgical maze procedure. It's the preferred AFib treatment for those who need another heart surgery. For example, it may be done during coronary artery bypass graft surgery or heart valve repair.
- Hybrid atrial fibrillation ablation. This therapy combines ablation with surgery. It is used to treat long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation.
- Pulsed field ablation. This is a treatment for some types of continued atrial fibrillation. It does not use heat or cold energy. Instead, it uses high-energy electric pulses to create areas of scar tissue in the heart. The scar tissue blocks faulty electrical signals that cause AFib.
Atrial fibrillation may return after cardiac ablation. If this happens, another ablation or heart treatment may be recommended. After cardiac ablation, blood thinners may be needed for life to prevent strokes.
If you have AFib but can't take blood thinners, a doctor may close a small sac in the left upper heart chamber. This sac is called an appendage. It's where most AFib-related clots form. This procedure is called left atrial appendage closure.
During left atrial appendage closure, a doctor gently guides a closure device through a catheter to the sac. Once the device is in place, the catheter is taken out. The device stays in permanently. This procedure also is an option for some people with AFib who are having another heart surgery.
More Information
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
A healthy lifestyle can help prevent or treat conditions that can lead to atrial fibrillation (AFib). Try the following steps to improve your heart health:
- Eat healthy foods. Choose plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Limit sugar, salt and saturated fats.
- Exercise and stay active. Regular physical activity helps control diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure — all risk factors for heart disease. Try to get 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Talk to your healthcare team about the amount and type of exercise that's best for you.
- Don't smoke or use tobacco. Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. If you need help quitting, talk to your healthcare team.
- Keep a healthy weight. Being overweight increases the risk of heart disease. Talk with your healthcare team to set realistic goals for weight.
- Control blood pressure. Get your blood pressure checked at least every two years if you're 18 and older. If you have risk factors for heart disease or are over age 40, you may need checks more often. If you have high blood pressure, follow your treatment plan as directed.
- Get your cholesterol checked. Ask your healthcare team how often you need a cholesterol test. Lifestyle changes and medicines may be recommended to control high cholesterol.
- Limit alcohol. Binge drinking, defined as having five drinks in two hours for men or four drinks for women, can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. In some people, even lower amounts of alcohol can trigger AFib.
- Practice good sleep habits. Poor sleep may increase the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. Adults should try to get 7 to 9 hours of sleep daily.
It also is important to have regular health checkups. Tell your healthcare team if your AFib symptoms get worse.
Preparing for your appointment
If you have an irregular or pounding heartbeat, make an appointment for a health checkup. If AFib is found early, treatment may be easier, and it may work better. You may be sent to a doctor trained in heart diseases. This type of doctor is called a cardiologist.
Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment.
What you can do
- Ask if there's anything you need to do before your appointment. For example, you may be told not to eat or drink for a few hours before a cholesterol test.
- Write down any symptoms you're having. Include any that may not seem related to atrial fibrillation. Note when they started, and what you were doing when they started.
- Write down important personal information. Include any family history of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure or diabetes. Also note any major stresses or recent life changes.
- Make a list of all medicines, vitamins or supplements that you're taking, even those bought without a prescription. Include the dosages.
- Take someone along, if possible. Someone who goes with you can help you remember information you're given.
- Write down questions to ask your healthcare team.
For atrial fibrillation, some basic questions to ask your doctor include:
- What is the likely cause of my symptoms or condition?
- What are other possible causes?
- What tests do I need?
- What's the most appropriate treatment?
- Is there a generic option to the medicine you're prescribing?
- What are other treatment options?
- What foods should I eat or not eat?
- How much exercise should I get? What is the safest type of exercise for me?
- Are there any other restrictions that I need to follow?
- How often should I be screened for heart disease or complications of AFib?
- I have other health conditions. How can I best manage them together?
- Should I see a specialist?
- Is there any information that I can take home with me? What websites do you recommend visiting?
Don't hesitate to ask any other questions during your appointment.
What to expect from your doctor
During a health checkup, you are usually asked many questions. Being ready to answer them may save time to go over any details you want to spend more time on. You may be asked:
- When did your symptoms start?
- Do you always have symptoms, or do they come and go?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, with 10 being the worst, how bad are your symptoms?
- What, if anything, seems to improve your symptoms?
- What, if anything, makes your symptoms worse?
What you can do in the meantime
It's never too early to make heart-healthy lifestyle changes. Eat healthy foods, stay active and don't smoke.
Jan. 14, 2026