Mayo Clinic's approach
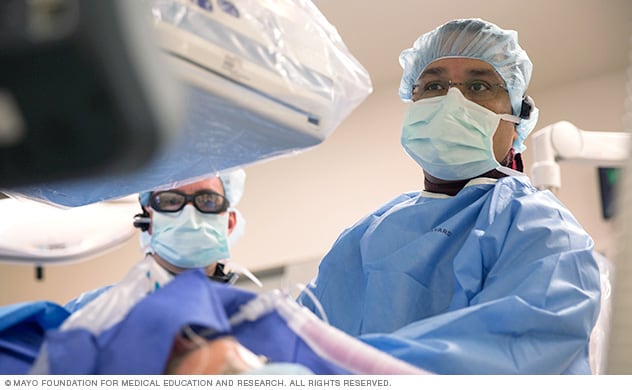 Cardiac catheter team performs an ablation
Cardiac catheter team performs an ablation
A Mayo Clinic doctor performs a cardiac ablation procedure in the electrophysiology laboratory.
At Mayo Clinic, experts in irregular heartbeats, called arrhythmias, provide compassionate, whole-person care to people considering atrial fibrillation ablation.
Experience you can trust
Cardiac ablation, including atrial fibrillation ablation, is done by heart doctors with special training in heart rhythm disorders. This type of healthcare professional is called an electrophysiologist. Mayo Clinic's skilled electrophysiologists work in the Electrophysiology Laboratory.
Mayo Clinic doctors perform every type of atrial fibrillation ablation. Studies show that cardiac ablation risks are lower when the treatment is done by an experienced electrophysiologist in a hospital that does many of the procedures.
Mayo Clinic doctors and researchers help shape best practices for the treatment of atrial fibrillation worldwide. They participate in meetings around the world to develop treatment guidelines for AFib.
 A team approach
A team approach
A doctor (right) works with an Electrophysiology Laboratory colleague to read a test result.
Collaborative approach to care
At Mayo Clinic, electrophysiologists work closely with other healthcare professionals, including cardiologists, pediatric cardiologists and cardiovascular surgeons, in the Heart Rhythm Clinic. The team works to understand your heart arrhythmia and recommend the best treatment options for you. Doctors trained in treating children with heart conditions, called pediatric cardiologists, work with other healthcare professionals to care for children with arrhythmias at Mayo Clinic's campus in Rochester, Minnesota. This team approach helps ensure that you or your child gets exactly the care that's needed.
The most advanced treatment systems
Mayo Clinic doctors do cardiac ablation using the latest and most advanced technologies.
Examples include advanced cardiac mapping systems such as multielectrode mapping and 3D heart mapping. The experienced team uses these methods during an electrophysiology (EP) study to decide where in the heart to do the cardiac ablation. Advanced mapping combined with intracardiac echocardiography lowers the exposure to radiation.
Your care professional chooses the type of cardiac ablation that's best for you and your health. Cardiac ablation uses heat energy, called radiofrequency energy, or cold energy, called cryoablation. The doctor applies the ablation using the latest innovations in treatment catheters and technology, such as balloon and robotic catheters.
 Learning about irregular heart rhythms, also called arrhythmias
Learning about irregular heart rhythms, also called arrhythmias
At Mayo Clinic, people learn about living with irregular heart rhythms, also called arrhythmias.
Expertise and rankings
Mayo Clinic electrophysiologists are recognized as experts in their field who have made important contributions to the understanding of arrhythmia diagnosis and treatment. Each year, about 2,000 people have cardiac ablation at Mayo Clinic.
Nationally recognized expertise
Mayo Clinic campuses are nationally recognized for expertise in cardiology and cardiovascular surgery:
- Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, Mayo Clinic in Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona, and Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida, are ranked among the Best Hospitals for heart and heart surgery by U.S. News & World Report.
- Mayo Clinic Children's in Rochester is ranked the No. 1 hospital in Minnesota and the five-state region of Iowa, Minnesota, North Dakota, South Dakota and Wisconsin, according to U.S. News & World Report's 2025-2026 "Best Children's Hospitals" rankings.
With Mayo Clinic's emphasis on collaborative care, specialists at each of the campuses — Minnesota, Arizona and Florida — work closely with colleagues at the other campuses and the Mayo Clinic Health System.
Learn more about Mayo Clinic's expertise and rankings in cardiovascular medicine.
Locations, travel and lodging
Mayo Clinic has major campuses in Phoenix and Scottsdale, Arizona; Jacksonville, Florida; and Rochester, Minnesota. The Mayo Clinic Health System has dozens of locations in several states.
For more information on visiting Mayo Clinic, choose your location below:
Costs and insurance
Mayo Clinic works with hundreds of insurance companies and is an in-network provider for millions of people.
In most cases, Mayo Clinic doesn't require a physician referral. Some insurers require referrals or may have additional requirements for certain medical care. All appointments are prioritized on the basis of medical need.
Learn more about appointments at Mayo Clinic.
Please contact your insurance company to verify medical coverage and to obtain any needed authorization prior to your visit. Often, your insurer's customer service number is printed on the back of your insurance card.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.