Overview
Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are sometimes used to mean the same thing. But there's a difference between the two terms.
Arteriosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from the heart to the rest of the body become thick and stiff. These blood vessels are called arteries. Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic. But over time, the walls in the arteries can harden, a condition commonly called hardening of the arteries.
Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls. This buildup is called plaque. The plaque can cause arteries to narrow, blocking blood flow. The plaque also can burst, leading to a blood clot.
Although atherosclerosis is often considered a heart condition, it can affect arteries anywhere in the body. Atherosclerosis can be treated. Healthy lifestyle habits can help prevent atherosclerosis.
Products & Services
Symptoms
Mild atherosclerosis usually doesn't cause symptoms.
Atherosclerosis symptoms usually don't happen until an artery is so narrowed or clogged that it can't send enough blood to organs and tissues. Sometimes a blood clot completely blocks blood flow. The clot may break apart. If this happens, it may cause a heart attack or stroke.
Symptoms of moderate to severe atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are affected. For example, if you have atherosclerosis:
- In your heart arteries, you may have chest pain or pressure, called angina.
- In the arteries leading to your brain, you may have sudden numbness or weakness in your arms or legs, trouble speaking, slurred speech, sudden or temporary loss of vision in one eye, or drooping muscles in your face. These are symptoms of a transient ischemic attack (TIA). Untreated, a TIA can lead to a stroke.
- In the arteries in your arms and legs, you may have leg pain when walking, called claudication. This is a symptom of peripheral artery disease (PAD). You also might have lower blood pressure in the affected arm or leg.
- In the arteries leading to your kidneys, you may get high blood pressure or kidney failure.
When to see a doctor
If you think you have atherosclerosis, make an appointment for a health checkup. Early diagnosis and treatment can stop atherosclerosis from getting worse. Treatment may prevent a heart attack, stroke or another medical emergency.
Get emergency medical help if you have chest pain or symptoms of transient ischemic attack or stroke such as:
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the arms or legs.
- Trouble speaking.
- Slurred speech.
- Sudden or temporary loss of vision in one eye.
- Drooping face muscles.
Causes
Development of atherosclerosis
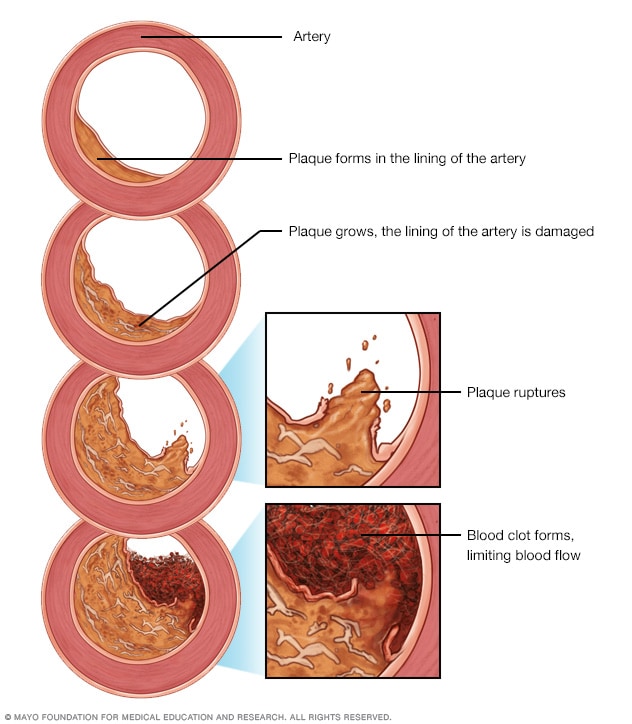
Development of atherosclerosis
If there's too much cholesterol in the blood, the cholesterol and other substances may form deposits called plaque. Plaque can cause an artery to become narrowed or blocked. If a plaque ruptures, a blood clot can form. Plaque and blood clots can reduce blood flow through an artery.
Atherosclerosis is a disease that slowly gets worse. It may begin as early as childhood. The exact cause is not known. It may start with damage or injury to the inner layer of an artery. Artery damage may be caused by:
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
- High triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood.
- Smoking or other tobacco use.
- Diabetes.
- Insulin resistance.
- Obesity.
- Inflammation from an unknown cause or from diseases such as arthritis, lupus, psoriasis or inflammatory bowel disease.
Once the inner wall of an artery is damaged, blood cells and other substances may collect at the injury site. These substances build up in the inner lining of the artery.
Over time, fats, cholesterol and other substances also collect on and in the walls of the heart arteries. This buildup is called plaque. Plaque can cause the arteries to narrow. Narrowed arteries can block blood flow. The plaque also can burst, leading to a blood clot.
Risk factors
Risk factors for atherosclerosis that you can't control include:
- Aging.
- A family history of early heart disease or stroke.
- Changes in genes that make atherosclerosis more likely.
- Having inflammatory conditions such as lupus, inflammatory bowel disease or psoriasis.
Risk factors for atherosclerosis that you may be able to control include:
- An unhealthy diet.
- Diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
- Lack of exercise.
- Obesity.
- Sleep apnea.
- Smoking and other tobacco use.
Complications
The complications of atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are narrowed or blocked. For example:
- Coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis in the arteries close to the heart can lead to coronary artery disease. This may cause chest pain, a heart attack or heart failure.
- Carotid artery disease. This is atherosclerosis in the arteries close to the brain. Complications include a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
- Peripheral artery disease. This is atherosclerosis in the arteries in the arms or legs. Complications include blocked or changed blood flow in the affected areas. Rarely, the lack of blood flow may cause tissue death, called gangrene.
- Aneurysms. Sometimes atherosclerosis can form a bulge in the wall of an artery. This is called an aneurysm. An aneurysm can occur anywhere in the body. Most people with aneurysms have no symptoms. If an aneurysm bursts, it can cause life-threatening bleeding inside the body.
- Chronic kidney disease. Atherosclerosis can cause the arteries leading to the kidneys to narrow. This prevents the kidneys from getting enough oxygen-rich blood. The kidneys need the blood flow to help remove fluids and waste products from the body.
Prevention
The same healthy lifestyle changes recommended to treat atherosclerosis also help prevent it. These lifestyle changes can help keep the arteries healthy:
- Do not smoke or use tobacco.
- Eat nutritious foods.
- Get regular exercise and keep an active lifestyle.
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Control blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol.
Sept. 20, 2024