Overview
Kidney cross section
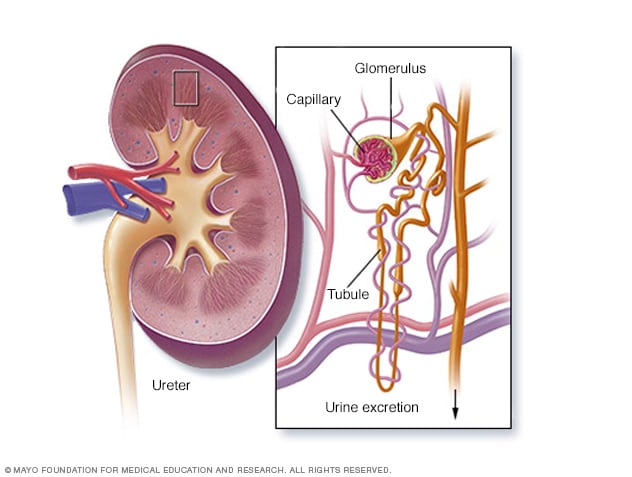
Kidney cross section
The kidneys remove waste and extra fluid from the blood through filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron contains a filter, called a glomerulus. Each filter has tiny blood vessels called capillaries. When blood flows into a glomerulus, tiny bits, called molecules, of water, minerals and nutrients, and wastes pass through the capillary walls. Large molecules, such as proteins and red blood cells, do not. The part that's filtered then passes into another part of the nephron called the tubule. The water, nutrients and minerals the body needs are sent back to the bloodstream. The extra water and waste become urine that flows to the bladder.
Glomerulonephritis (gloe-MER-u-loe-nuh-FRY-tis) is inflammation of the tiny filters in the kidneys (glomeruli). The excess fluid and waste that glomeruli (gloe-MER-u-lie) remove from the bloodstream exit the body as urine. Glomerulonephritis can come on suddenly (acute) or gradually (chronic).
Glomerulonephritis occurs on its own or as part of another disease, such as lupus or diabetes. Severe or prolonged inflammation associated with glomerulonephritis can damage the kidneys. Treatment depends on the type of glomerulonephritis you have.
Products & Services
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of glomerulonephritis may vary depending on whether you have the acute or chronic form and the cause. You may notice no symptoms of chronic disease. Your first indication that something is wrong might come from the results of a routine urine test (urinalysis).
Glomerulonephritis signs and symptoms may include:
- Pink or cola-colored urine from red blood cells in your urine (hematuria).
- Foamy or bubbly urine due to excess protein in the urine (proteinuria).
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- Fluid retention (edema) with swelling evident in your face, hands, feet and abdomen.
- Urinating less than usual.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Muscle cramps.
- Fatigue.
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your health care provider promptly if you have signs or symptoms of glomerulonephritis.
Causes
Many conditions can cause glomerulonephritis. Sometimes the disease runs in families and sometimes the cause is unknown. Factors that can lead to inflammation of the glomeruli include the following conditions.
Infections
Infectious diseases can directly or indirectly lead to glomerulonephritis. These infections include:
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Glomerulonephritis may develop a week or two after recovery from a strep throat infection or, rarely, a skin infection caused by a streptococcal bacteria (impetigo). Inflammation occurs when antibodies to the bacteria build up in the glomeruli. Children are more likely to develop post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis than are adults, and they're also more likely to recover quickly.
- Bacterial endocarditis. Bacterial endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of your heart's chambers and valves. It isn't clear whether the inflammation in the kidneys is the result of immune system activity alone or other factors.
- Viral kidney infections. Viral infections of the kidney, such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C, cause inflammation of the glomeruli and other kidney tissues.
- HIV. Infection with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, can lead to glomerulonephritis and progressive kidney damage, even before the onset of AIDS.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases are illnesses caused by the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Autoimmune diseases that may cause glomerulonephritis include:
- Lupus. A chronic inflammatory disease, systemic lupus erythematosus can affect many parts of your body, including your skin, joints, kidneys, blood cells, heart and lungs.
- Goodpasture's syndrome. In this rare disorder, also known as anti-GBM disease, the immune system creates antibodies to tissues in the lungs and kidneys. It can cause progressive and permanent damage to the kidneys.
- IgA nephropathy. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is an antibody that's a first line of defense against infectious agents. IgA nephropathy occurs when deposits of the antibody accumulate in the glomeruli. The inflammation and subsequent damage may go undetected for a long time. The most common symptom is blood in the urine.
Vasculitis
Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels. Types of vasculitis that can cause glomerulonephritis include:
- Polyarteritis. This form of vasculitis affects medium and small blood vessels in many parts of your body, including the kidneys, skin, muscles, joints and digestive tract.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis. This form of vasculitis, formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis, affects small and medium blood vessels in your lungs, upper airways and kidneys.
Sclerotic conditions
Some diseases or conditions cause scarring of the glomeruli that results in poor and declining kidney function. These include:
- High blood pressure. Long-term, poorly managed high blood pressure can cause scarring and inflammation of the glomeruli. Glomerulonephritis inhibits the kidney's role in regulating blood pressure.
- Diabetic kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy). High blood sugar levels contribute to scarring of the glomeruli and increase the rate of blood flow through the nephrons.
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. In this condition, scarring is scattered among some of the glomeruli. This may be the result of another disease, or it may occur for no known reason.
Other causes
Infrequently, chronic glomerulonephritis runs in families. One inherited form, Alport syndrome, also might impair hearing or vision.
Glomerulonephritis is associated with certain cancers, such as gastric cancer, lung cancer and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Risk factors
Some autoimmune diseases are linked with glomerulonephritis.
Complications
Glomerulonephritis affects the ability of nephrons to filter the bloodstream efficiently. The breakdown in filtering results in:
- Accumulation of wastes or toxins in the bloodstream.
- Poor regulation of essential minerals and nutrients.
- Loss of red blood cells.
- Loss of blood proteins.
Possible complications of glomerulonephritis include:
- Acute kidney failure. Acute kidney failure is the sudden, rapid decline in kidney function, often associated with an infectious cause of glomerulonephritis. The accumulation of waste and fluids can be life-threatening if not treated promptly with an artificial filtering machine (dialysis). The kidneys often resume typical function after recovery.
- Chronic kidney disease. Persistent inflammation results in long-term damage and declining function of the kidneys. Chronic kidney disease is generally defined as kidney damage or decreased function for three or more months. Chronic kidney disease may advance to end-stage kidney disease, which requires either dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- High blood pressure. Damage to the glomeruli from inflammation or scarring can lead to increased blood pressure.
- Nephrotic syndrome. Nephrotic syndrome is a condition in which there is too much blood protein in urine and too little in the bloodstream. These proteins play a role in regulating fluids and cholesterol levels. A drop in blood proteins results in high cholesterol, high blood pressure and swelling (edema) of the face, hands, feet and abdomen. In rare instances, nephrotic syndrome may cause a blood clot in a kidney blood vessel.
Prevention
There may be no way to prevent some forms of glomerulonephritis. However, here are some steps that might be beneficial:
- Seek prompt treatment of a strep infection with a sore throat or impetigo.
- To prevent infections that can lead to some forms of glomerulonephritis, such as HIV and hepatitis, follow safe-sex guidelines and avoid intravenous drug use.
- Control high blood pressure, which lessens the likelihood of damage to your kidneys from hypertension.
- Control your blood sugar to help prevent diabetic nephropathy.
Feb. 24, 2024