概述
肢端肥大症患者
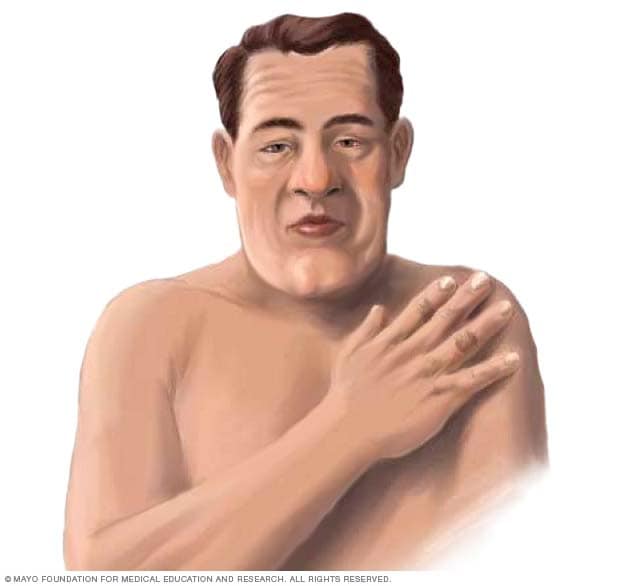

肢端肥大症患者
肢端肥大症的症状包括面部和手部增大。面部变化可能导致眉骨和下颌骨突出,鼻子和嘴唇变大。
肢端肥大症是一种罕见的成人状况,会导致某些骨骼、器官和其他组织变大。这些变化是由垂体(脑中的小腺体)分泌过多生长激素所致。这往往是由于垂体中出现了肿瘤。肿瘤并非癌变。
当体内生长激素过多时,骨骼就会变大。如果发生在儿童时期,这会导致身高剧增——巨人症的症状。如果成人患肢端肥大症,身高不会发生变化。而是手、足和面部的骨骼变大。
这些变化是在很多年内缓慢发生的。因此,肢端肥大症患者及其亲人可能需要很长时间才会发现症状,而医疗护理专业人员可能也很难在早期发现和治疗这种疾病。
如果不予治疗,肢端肥大症可能会引起其他严重的、有时甚至危及生命的健康状况(称为并发症)。但手术、药物和放疗等治疗可以降低出现并发症的风险。治疗还可以改善许多肢端肥大症症状。
症状
肢端肥大症的症状可能会改变某些身体部位的外观。变化可能包括:
- 耳朵和嘴唇增厚。
- 鼻子变宽。
- 手脚变大。
- 额头或颚突出。
- 牙齿之间出现缝隙。
- 舌头变大。
- 肋廓扩张可能导致胸部外观呈圆形。
皮肤变化可能包括:
- 痤疮。
- 无害性皮肤赘生物(即皮赘)。
- 皮肤变粗糙、油腻、增厚。
- 皮下组织肿胀。
患有肢端肥大症的人通常不会出现所有可能的身体变化。由于这些变化发生缓慢,可能需要多年才被发现。但随着时间推移,手指上的戒指可能不再像以前一样合适。鞋码可能变大。有时,人们只有在对比新旧照片时才能发现变化。
肢端肥大症的其他症状可能包括:
- 视力问题,包括周边视力丧失。
- 出汗增多和体味异常明显。
- 极度疲倦。
- 头痛。
- 关节疼痛。
- 声音变低沉。
How does acromegaly affect the body?
Beyond visible changes, too much GH and IGF-1 affect many organs and systems. Specific effects include:
- Dental health. Acromegaly can cause an unusually large jaw and spacing between the teeth. People may notice gaps forming between teeth, bite changes or teeth that don't line up correctly. The tongue also may enlarge, leading to speech and breathing problems. Regular dental care is important for managing these oral changes.
- Reproductive and sexual health. Excess growth hormone can affect reproductive health. In men, acromegaly may lead to erectile dysfunction, reduced libido and low testosterone. Enlargement of soft tissues also may occur, but sexual issues are usually due to hormonal imbalance rather than physical enlargement.
- Voice changes. Thickening of tissues in the vocal cords and throat can make the voice deeper or hoarser over time. Some people also notice snoring or changes in speech.
Early symptoms of acromegaly may be subtle, such as changes in ring or shoe size. As the condition progresses, other common symptoms can include:
- Vision troubles, including loss of side vision.
- More sweating and body odor than is typical.
- Fatigue and low energy.
- Headaches.
- Joint pain.
- Sleep problems, including sleep apnea.
What is the difference between acromegaly and other conditions?
Acromegaly is a rare hormonal condition in adults that happens when there is too much growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). Acromegaly is usually caused by a noncancerous, also called benign, pituitary tumor. It leads to enlarged hands, feet and facial features, joint pain, and serious complications if it's not treated. Several other conditions may look similar to acromegaly, but the causes and symptoms are different.
Acromegaly vs. gigantism
- Gigantism happens when too much growth hormone is produced before puberty while the bones are still growing.
- Children with gigantism grow unusually tall, with very long arms and legs.
- Acromegaly develops after puberty, when the growth plates are closed. It causes changes in hands, feet and facial bones, but not extreme height.
Acromegaly vs. Cushing disease
- Cushing disease is caused by too much cortisol. Cortisol is another pituitary hormone. The extra cortisol changes where fat is stored.
- Symptoms include weight gain in the face and trunk, a hump on the back from the redistributed fat storage, easy bruising and diabetes.
- Acromegaly is caused by too much of the GH and IGF-1 hormones and leads to bone and tissue overgrowth, not fat redistribution.
Acromegaly vs. Marfan syndrome
- Marfan syndrome is a genetic condition that affects connective tissue.
- People with Marfan syndrome are tall and thin with long arms, legs and fingers, and heart or eye conditions.
- Acromegaly develops later in life and does not cause the long, slender build of Marfan syndrome.
Acromegaly vs. Paget's disease of bone
- Paget's disease is a condition where bones break down and regrow in an unusual way, becoming weak and misshapen.
- It can cause skull enlargement, bent legs or bone pain.
- Unlike Paget's disease of bone, acromegaly also causes soft tissue swelling, enlarged hands and feet, and metabolic complications such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and sleep apnea.
Acromegaly vs. achondroplasia
- Achondroplasia is the most common form of dwarfism. It is caused by a gene change that affects bone growth.
- People with achondroplasia have short stature, short arms and legs, and an average-sized trunk.
- Acromegaly does not cause short stature. Instead, it causes enlargement of features after typical growth is complete.
Acromegaly vs. Weaver syndrome
- Weaver syndrome is a very rare condition present from birth that causes rapid growth, advanced bone age and developmental delays. Weaver syndrome is caused by a change in a gene and is passed down from a parent to a child.
- Babies and children with Weaver syndrome are tall and large for their age.
- Acromegaly develops in adulthood and is not caused by a gene change.
何时就诊
如果您认为自己有肢端肥大症的症状,请进行健康检查。该状况通常进展缓慢,即使家庭成员可能也需要很长时间才能注意到所发生的身体变化。但是,能让医务人员尽早发现该状况仍至关重要。治疗可以帮助预防伴随肢端肥大症发生的严重健康状况。
病因
垂体腺和下丘脑
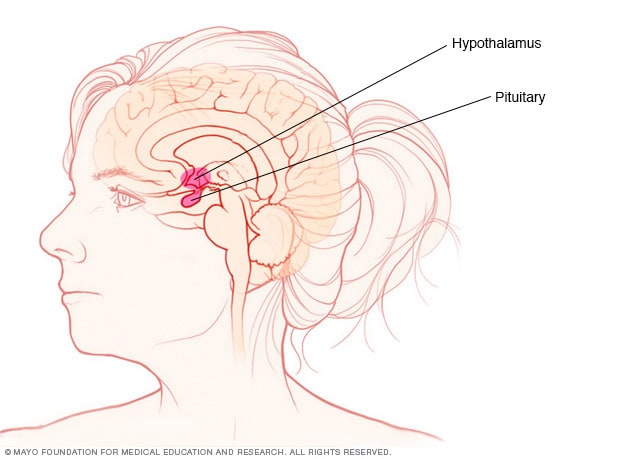
垂体腺和下丘脑
垂体和下丘脑位于脑中。它们产生的激素控制着体内的许多重要功能。
肢端肥大症的最常见病因是垂体瘤。这个肿瘤被称为腺瘤。并非癌症。但它会在很长一段时间内分泌过多生长激素。
生长激素过多会导致肢端肥大症的诸多症状。肢端肥大症的某些症状(例如头痛和视力受损)是由肿瘤压迫附近脑组织所致。
在极少数情况下,身体其他部位的肿瘤也可能引发肢端肥大症。包括肺部或胰腺肿瘤。有时这些肿瘤会分泌生长激素。也可能分泌一种被称为生长激素释放激素的激素。这种激素会向垂体发出信号,促使其分泌更多的生长激素。
垂体位于大脑底部,处于鼻梁后方。它分泌生长激素和其他激素。生长激素在调控身体发育方面发挥重要作用。
垂体释放生长激素进入血液。这会刺激肝脏生成一种称为胰岛素样生长因子-1(IGF-1)的激素。IGF-1 是促使骨骼和其他组织生长的主要因素。生长激素过多会导致 IGF-1 过量,从而引发肢端肥大症的症状和并发症。
What is the relationship between pituitary tumors and acromegaly?
Acromegaly is almost always caused by a pituitary adenoma, which is a noncancerous tumor that develops in the pituitary gland. Pituitary adenomas are the most common type of pituitary tumor. Pituitary adenomas and other tumors are types of skull base tumors.
The pituitary gland contains different types of hormone-producing cells, including somatotroph cells. Somatotroph cells make growth hormone (GH). When a tumor grows from the somatotroph cells, it can release too much GH. Extra GH causes the liver to make more insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). This leads to the body changes seen in acromegaly such as enlarged hands, feet and facial features. Only somatotroph adenomas, sometimes called GH-secreting adenomas, cause acromegaly.
Other types of pituitary adenomas come from different hormone-producing cells, but these do not cause acromegaly:
- Lactotroph adenomas make prolactin and can cause issues such as irregular periods and difficulty getting pregnant.
- Corticotroph adenomas make adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Too much ACTH causes the adrenal glands to release extra cortisol, which can lead to Cushing disease.
- Thyrotroph adenomas make thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and can lead to hyperthyroidism.
- Gonadotroph adenomas usually do not make excess hormone. But as they grow, gonadotroph adenomas can press on nearby tissues and cause symptoms such as headaches, vision problems, low energy, or changes in sexual and reproductive health.
风险因素
多发性内分泌腺瘤病 1 型这一罕见遗传状况患者有更高风险出现肢端肥大症。多发性内分泌腺瘤病 1 型又称 MEN 1。
患有 MEN 1 时,甲状旁腺、胰腺和垂体可能会长肿瘤并释放额外的激素。额外的甲状旁腺素可能导致骨质疏松和肾结石。胰腺肿瘤可能会产生激素胰岛素并导致低血糖。如果垂体瘤分泌额外的生长激素,会导致肢端肥大症。在极少数情况下,肢端肥大症会在家族中遗传。
并发症
如果不治疗,肢端肥大症可能会引发其他健康问题(称为并发症)。其中可能包括以下并发症。
心脏和血管状况,例如:
- 高血压。
- 动脉变窄的风险增加,这可能导致心脏病发作或卒中。
- 心肌疾病(心肌病)。
癌症及可能导致癌症的状况:
- 患某些癌症的风险更高。
- 结肠内膜上有称为息肉的生长物。如果不治疗,这些生长物可能会发展为结肠癌。
性病和生殖系统疾病,例如:
- 不来月经或不规律阴道出血。
- 勃起困难或无法保持勃起(勃起功能障碍)。
- 性欲降低。
其他严重状况包括:
- 最常见类型的关节炎,即骨关节炎。
- 2 型糖尿病。
- 甲状腺中的不规则生长物,称为甲状腺肿。
- 睡眠呼吸暂停,这是睡眠期间多次出现呼吸暂停然后恢复的一种状况。
- 腕管综合征, 一种可引起手部和手臂麻木感、刺痛和无力的状况。
- 脊髓受压或骨折。
- 视力改变或视力丧失。
尽早治疗肢端肥大症可以预防这些并发症的发生或恶化。如果不治疗,肢端肥大症及其并发症可能导致早逝。
Heart and blood vessel complications
Cancer and conditions that can lead to cancer
- Higher risk of some cancers, including prostate, breast, colon, thyroid and stomach cancer.
- Growths called polyps on the lining of the colon. Without treatment, these growths can lead to colon cancer.
Sexual health, reproductive health and pregnancy concerns
Metabolic problems
Bone, joint and nerve conditions
Other complications
- Sleep apnea, which is a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- Changes in the thyroid gland, called a goiter.
- Vision changes or vision loss if the tumor presses on the optic nerves.
- Depression (major depressive disorder), fatigue and reduced quality of life.
Early treatment of acromegaly can prevent these complications or keep them from becoming worse. Without treatment, acromegaly and its complications can shorten life expectancy.