Overview
Diskectomy
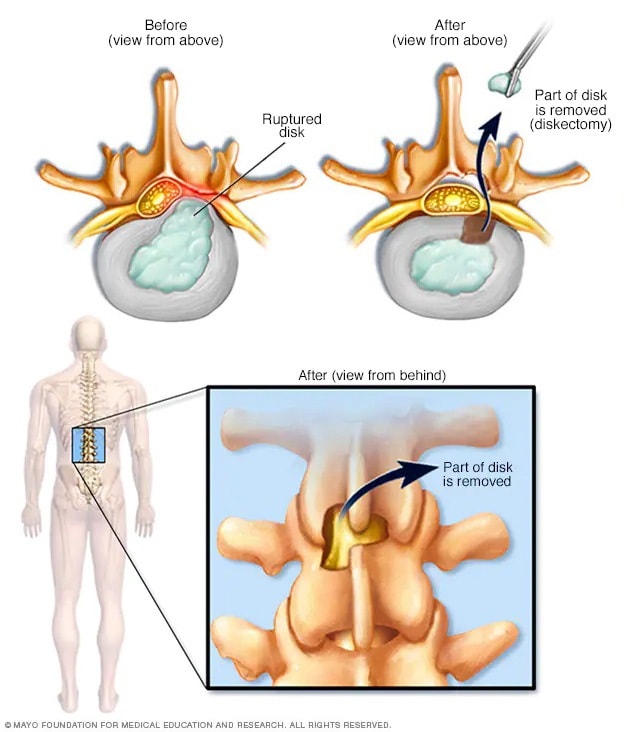
Diskectomy
Diskectomy is the surgical removal of the damaged portion of a herniated disk in the spine. A herniated disk occurs when some of the softer material inside the disk pushes out through a crack in the tougher outside of the disk. This can irritate or press on nearby nerves and cause pain, numbness or weakness.
Diskectomy is surgery to remove the damaged part of a disk in the spine. A diskectomy can relieve the pressure caused by a herniated disk. A herniated disk happens when the soft center of a disk pushes out through the tough outer lining. Herniated disks can irritate or press on nearby nerves.
Diskectomy works best for treating pain that travels down the arms or legs from a compressed nerve. The procedure is less helpful for treating pain that's felt only in the back or neck. Most people who have back pain or neck pain find relief with other treatments, such as weight loss, arthritis medicines or physical therapy.
A healthcare professional might suggest diskectomy if other, nonsurgical treatments have not worked or if symptoms worsen. There are several ways to perform a diskectomy. Many surgeons prefer minimally invasive diskectomy, which uses small incisions and a microscope or tiny video camera for viewing the procedure.
Products & Services
Why it's done
A diskectomy is done to relieve the pressure a herniated disk places on a spinal nerve. A herniated disk occurs when some of the softer material inside the disk pushes out through a crack in the outer lining of the disk. A herniated disk also is called a slipped, ruptured or bulging disk or disk prolapse.
A healthcare professional might recommend diskectomy if:
- Nerve weakness causes trouble standing or walking.
- Conservative treatment, such as physical therapy or steroid injections, fails to improve symptoms after 6 to 12 weeks.
- Pain travels into the butt, legs, arms or chest and becomes too much to manage.
Risks
Diskectomy is considered safe. But as with any surgery, diskectomy carries a risk of complications. Potential complications include:
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- Leaking spinal fluid.
- Injury to blood vessels or nerves in and around the spine.
How you prepare
You'll likely need to avoid eating and drinking for a certain amount of time before surgery. If you take blood-thinning medicines, you may need to adjust how much you take before surgery. Your healthcare team can give you specific instructions.
What you can expect
During diskectomy
Surgeons usually perform diskectomy using general anesthesia, so you're not awake during the surgery. Ideally, just the piece of disk that's compressing the nerve is removed. However, small amounts of spinal bone and ligament might need to be removed to get to the herniated disk.
If the whole disk must be taken out, your surgeon may need to fill the space with a piece of bone. The replacement bone may come from a deceased donor or from your own pelvis, or the surgeon may use a synthetic bone substitute. The adjoining spinal bones, called vertebrae, are then fused together.
After diskectomy
After surgery, you're moved to a recovery room where the healthcare team watches for complications from the surgery and anesthesia. You might be able to go home the day of surgery. But a short hospital stay might be needed, especially for people who have serious medical conditions.
Depending on the amount of lifting, walking and sitting your job involves, you may be able to return to work in 2 to 6 weeks. If you have a job that includes heavy lifting or operating heavy machinery, you might have to wait 6 to 8 weeks before returning to work.
Results
Diskectomy reduces herniated disk symptoms in most people who have clear symptoms of a compressed nerve, such as pain that travels down the legs. However, relief from a diskectomy might not last a lifetime because it doesn't cure the cause of the disk becoming injured or herniated in the first place.
To help prevent re-injury of the spine, it may help to keep a healthy weight, eat a healthy diet, do low-impact exercises, and limit activities that involve repeated bending, twisting or lifting.