概述
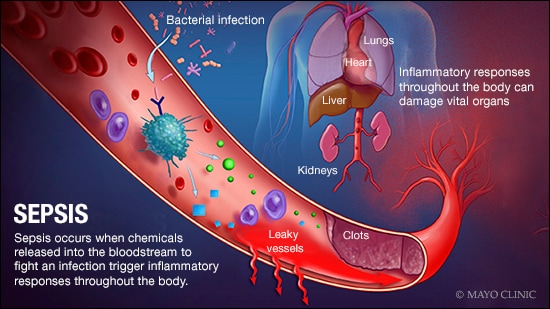
脓毒症是一种身体对感染反应异常的严重疾病。身体启动抗感染过程,导致器官功能不良。
脓毒症可能进展为感染性休克,导致血压骤降,会损害肺、肾、肝和其他器官,严重时甚至可能导致死亡。
尽早治疗脓毒症可以提高生存率。
症状
脓毒症的症状
脓毒症的症状可能包括:
- 精神状态改变。
- 浅快呼吸。
- 不明原因导致的出汗。
- 感觉头重脚轻。
- 战栗。
- 不同感染类型的特定症状,例如尿路感染导致的排尿疼痛、感染性肺炎导致的咳嗽加重。
脓毒症的症状不具特异性。可能因人而异,而且儿童和成人的脓毒症表现可能不同。
感染性休克的症状
脓毒症可能会进展为感染性休克。感染性休克是指血压大幅下降。进展为感染性休克会增加死亡的风险。感染性休克的症状包括:
- 无法站起来。
- 睡意强烈或难以保持清醒。
- 精神状态发生重大变化,例如极度意识模糊。
何时就诊
任何感染均可能导致脓毒症。如果您出现脓毒症的症状,或者感染或伤口不见好转,请就医。
如果出现意识模糊或呼吸急促等症状,则需要急救护理。
病因
任何类型的感染都可能引起脓毒症,包括细菌、病毒或真菌感染。以下部位的感染更常引起脓毒症:
- 肺部,如感染性肺炎。
- 肾脏、膀胱和泌尿系统其他部位。
- 消化系统。
- 血流。
- 插管部位。
- 伤口或烧伤部位。
风险因素
增加感染引发脓毒症的风险的一些因素包括:
- 年满 65 岁。
- 婴儿。
- 免疫力低下者,如正在接受癌症治疗的人或 HIV 感染者。
- 慢性病(如糖尿病、肾病或 COPD)患者。
- 入住重症监护室或住院时间较长。
- 有医疗器械置入体内,如静脉导管或呼吸管。
- 过去 90 天内接受过抗生素治疗。
- 存在需要用皮质类固醇治疗的医疗状况,皮质类固醇可能降低免疫反应。
并发症
随着脓毒症的恶化,重要器官(如脑、心脏和肾脏)获得的血流减少。脓毒症可能导致非典型凝血。因此产生的小血凝块或血管破裂可能损伤或破坏组织。
大多数人可从轻度脓毒症中恢复,但感染性休克的死亡率约为 30% 至 40%。此外,严重的脓毒症发作会增加未来感染的风险。