Overview
Cold sore
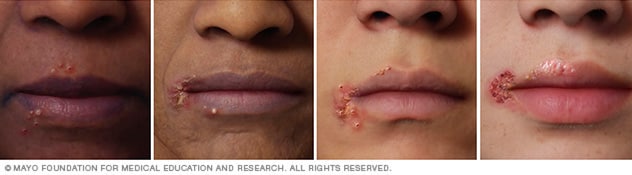
Cold sore
Illustration of cold sore on different skin colors. A cold sore is a cluster of fluid-filled blisters. Healing often occurs in two to three weeks without scarring. Cold sores are sometimes called fever blisters.
Cold sores, or fever blisters, are a common viral infection. They are tiny, fluid-filled blisters on and around the lips. These blisters are often grouped together in patches. After the blisters break, a scab forms that can last several days. Cold sores usually heal in 2 to 3 weeks without leaving a scar.
Cold sores spread from person to person by close contact, such as kissing. They're usually caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), and less commonly herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). Both of these viruses can affect the mouth or genitals and can be spread by oral sex. The virus can spread even if you don't see the sores.
There's no cure for cold sores, but treatment can help manage outbreaks. Prescription antiviral medicine or creams can help sores heal more quickly. And they may make future outbreaks happen less often and be shorter and less serious.
Symptoms
A cold sore usually passes through several stages:
- Tingling and itching. Many people feel itching, burning or tingling around the lips for a day or so before a small, hard, painful spot appears and blisters form.
- Blisters. Small fluid-filled blisters often form along the border of the lips. Sometimes they appear around the nose or cheeks or inside the mouth.
- Oozing and crusting. The small blisters may merge and then burst. This can leave shallow open sores that ooze and crust over.
Symptoms vary, depending on whether this is your first outbreak or a recurrence. The first time you have a cold sore, symptoms may not start for up to 20 days after you were first exposed to the virus. The sores can last several days. And the blisters can take 2 to 3 weeks to heal completely. If blisters return, they'll often appear at the same spot each time and tend to be less severe than the first outbreak.
In a first-time outbreak, you also might experience:
- Fever.
- Painful gums.
- Sore throat.
- Headache.
- Muscle aches.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
Children under 5 years old may have cold sores inside their mouths. These sores are often mistaken for canker sores. Canker sores involve only the mucous membrane and aren't caused by the herpes simplex virus.
When to see a doctor
Cold sores generally clear up without treatment. See your health care provider if:
- You have a weak immune system.
- The cold sores don't heal within two weeks.
- Symptoms are severe.
- The cold sores often return.
- You have gritty or painful eyes.
Causes
Cold sores are caused by certain strains of the herpes simplex virus (HSV). HSV-1 usually causes cold sores. HSV-2 is often the cause of genital herpes. But either type can spread to the face or genitals through close contact, such as kissing or oral sex. Shared eating utensils, razors and towels can also spread HSV-1.
Cold sores are most likely to spread when you have oozing blisters. But you can spread the virus even if you don't have blisters. Many people who are infected with the virus that causes cold sores never develop symptoms.
Once you've had a herpes infection, the virus can hide in nerve cells in the skin and may cause another cold sore at the same place as before. A return of cold sores may be triggered by:
- Viral infection or fever.
- Hormonal changes, such as those related to a menstrual period.
- Stress.
- Fatigue.
- Being in the sun or wind.
- Changes in the immune system.
- Injury to the skin.
Video: 3 things you didn't know about cold sores
Ian Roth: Cold sores on the lips can be embarrassing and tough to hide. But, turns out, you might not have a reason to be embarrassed.
Pritish Tosh, M.D., Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic: About 70-plus percent of the U.S. population has been infected with herpes simplex 1. Now, a very small percentage of those people will actually develop cold sores.
Ian Roth: Dr. Pritish Tosh, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic, says genetics determines whether a person will develop cold sores.
Dr. Tosh: A proportion of the population, they don't quite have the right immunologic genes and things like that and so they're not able to handle the virus as well as other people in the population.
Ian Roth: The problem is people can spread the herpes virus whether they develop cold sores or not. Herpes virus spreads through physical contact like kissing, sharing a toothbrush — even sharing a drinking glass — or through sexual contact.
Dr. Tosh: Since the number of people who are infected but don't have symptoms vastly outnumber the people who are infected and have symptoms, most new transmissions occur from people who have no idea that they are infected.
For the Mayo Clinic News Network, I'm Ian Roth.
Risk factors
Almost everyone is at risk of cold sores. Most adults carry the virus that causes cold sores, even if they've never had symptoms.
You're most at risk of complications from the virus if you have a weak immune system from conditions and treatments such as:
- HIV/AIDS.
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema).
- Cancer chemotherapy.
- Anti-rejection medicine for organ transplants.
Complications
In some people, the virus that causes cold sores can cause problems in other areas of the body, including:
- Fingertips. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can be spread to the fingers. This type of infection is often referred to as herpes whitlow. Children who suck their thumbs may transfer the infection from their mouths to their thumbs.
- Eyes. The virus can sometimes cause eye infection. Repeated infections can cause scarring and injury, which may lead to vision problems or loss of vision.
- Widespread areas of skin. People who have a skin condition called atopic dermatitis (eczema) are at higher risk of cold sores spreading all across their bodies. This can become a medical emergency.
Prevention
Your health care provider may prescribe an antiviral medicine for you to take on a regular basis if you develop cold sores more than nine times a year or if you're at high risk of serious complications. If sunlight seems to trigger your condition, apply sunblock to the spot where the cold sore tends to form. Or talk with your health care provider about using an oral antiviral medicine before you do an activity that tends to cause a cold sore to return.
Take these steps to help avoid spreading cold sores to other people:
- Avoid kissing and skin contact with people while blisters are present. The virus spreads most easily when the blisters leak fluid.
- Avoid sharing items. Utensils, towels, lip balm and other personal items can spread the virus when blisters are present.
- Keep your hands clean. When you have a cold sore, wash your hands carefully before touching yourself and other people, especially babies.
Jan. 05, 2024