Overview
Canker sore
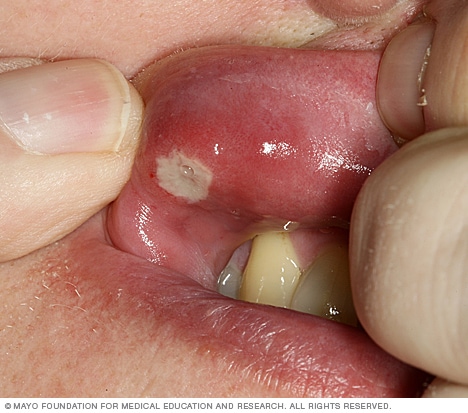
Canker sore
Canker sores occur singly or in clusters on the inside surfaces of your cheeks or lips, on or under your tongue, at the base of your gums, or on your soft palate. They usually have a white or yellow center and a red border and can be extremely painful.
Canker sores, also called aphthous ulcers, are small, shallow lesions that develop on the soft tissues in your mouth or at the base of your gums. Unlike cold sores, canker sores don't occur on the surface of your lips and they aren't contagious. They can be painful, however, and can make eating and talking difficult.
Most canker sores go away on their own in a week or two. Check with your doctor or dentist if you have unusually large or painful canker sores or canker sores that don't seem to heal.
Symptoms
Most canker sores are round or oval with a white or yellow center and a red border. They form inside your mouth — on or under your tongue, inside your cheeks or lips, at the base of your gums, or on your soft palate. You might notice a tingling or burning sensation a day or two before the sores actually appear.
There are several types of canker sores, including minor, major and herpetiform sores.
Minor canker sores
Minor canker sores are the most common and:
- Are usually small
- Are oval shaped with a red edge
- Heal without scarring in one to two weeks
Major canker sores
Major canker sores are less common and:
- Are larger and deeper than minor canker sores
- Are usually round with defined borders, but may have irregular edges when very large
- Can be extremely painful
- May take up to six weeks to heal and can leave extensive scarring
Herpetiform canker sores
Herpetiform canker sores are uncommon and usually develop later in life, but they're not caused by herpes virus infection. These canker sores:
- Are pinpoint size
- Often occur in clusters of 10 to 100 sores, but may merge into one large ulcer
- Have irregular edges
- Heal without scarring in one to two weeks
When to see a doctor
Consult your doctor if you experience:
- Unusually large canker sores
- Recurring sores, with new ones developing before old ones heal, or frequent outbreaks
- Persistent sores, lasting two weeks or more
- Sores that extend into the lips themselves (vermilion border)
- Pain that you can't control with self-care measures
- Extreme difficulty eating or drinking
- High fever along with canker sores
See your dentist if you have sharp tooth surfaces or dental appliances that seem to trigger the sores.
Causes
The precise cause of canker sores remains unclear, though researchers suspect that a combination of factors contributes to outbreaks, even in the same person.
Possible triggers for canker sores include:
- A minor injury to your mouth from dental work, overzealous brushing, sports mishaps or an accidental cheek bite
- Toothpastes and mouth rinses containing sodium lauryl sulfate
- Food sensitivities, particularly to chocolate, coffee, strawberries, eggs, nuts, cheese, and spicy or acidic foods
- A diet lacking in vitamin B-12, zinc, folate (folic acid) or iron
- An allergic response to certain bacteria in your mouth
- Helicobacter pylori, the same bacteria that cause peptic ulcers
- Hormonal shifts during menstruation
- Emotional stress
Canker sores may also occur because of certain conditions and diseases, such as:
- Celiac disease, a serious intestinal disorder caused by a sensitivity to gluten, a protein found in most grains
- Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
- Behcet's disease, a rare disorder that causes inflammation throughout the body, including the mouth
- A faulty immune system that attacks healthy cells in your mouth instead of pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria
- HIV/AIDS, which suppresses the immune system
Unlike cold sores, canker sores are not associated with herpes virus infections.
Risk factors
Anyone can develop canker sores. But they occur more often in teens and young adults, and they're more common in females.
Often people with recurrent canker sores have a family history of the disorder. This may be due to heredity or to a shared factor in the environment, such as certain foods or allergens.
Prevention
Canker sores often recur, but you may be able to reduce their frequency by following these tips:
- Watch what you eat. Try to avoid foods that seem to irritate your mouth. These may include nuts, chips, pretzels, certain spices, salty foods and acidic fruits, such as pineapple, grapefruit and oranges. Avoid any foods to which you're sensitive or allergic.
- Choose healthy foods. To help prevent nutritional deficiencies, eat plenty of fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Follow good oral hygiene habits. Regular brushing after meals and flossing once a day can keep your mouth clean and free of foods that might trigger a sore. Use a soft brush to help prevent irritation to delicate mouth tissues, and avoid toothpastes and mouth rinses that contain sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Protect your mouth. If you have braces or other dental appliances, ask your dentist about orthodontic waxes to cover sharp edges.
- Reduce your stress. If your canker sores seem to be related to stress, learn and use stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation and guided imagery.